CPU GPU Bottleneck Calculator & Checker for Gaming (2026)
You spent $800 on a GPU. Your games still stutter. You drop frames at the worst moments. Your FPS numbers look fine on paper, but in-game it feels like you're gaming through molasses. Sound familiar? That gap between "specs look good" and "performance feels terrible" is almost always a bottleneck — and most gamers don't even know they have one until they've already wasted money on the wrong upgrade. Our CPU GPU Bottleneck Calculator is built for exactly this moment. It's a free, no-sign-up, online PC compatibility checker that gives you a clear bottleneck percentage, a hardware balance verdict, and actionable upgrade suggestions — whether you're running a $500 entry-level rig or a $3,000 beast.
Wondering "am I bottlenecked?" or "where's my bottleneck?" — you're in the right place. isitBOTTLENECKED is a free bottleneck checker and bottleneck tester that goes beyond a simple percentage. Enter your CPU, GPU, RAM, and resolution to instantly check CPU-GPU compatibility, run a full PC bottleneck test, and find out exactly what's holding your gaming rig back.
How to Check if Your PC is Bottlenecked
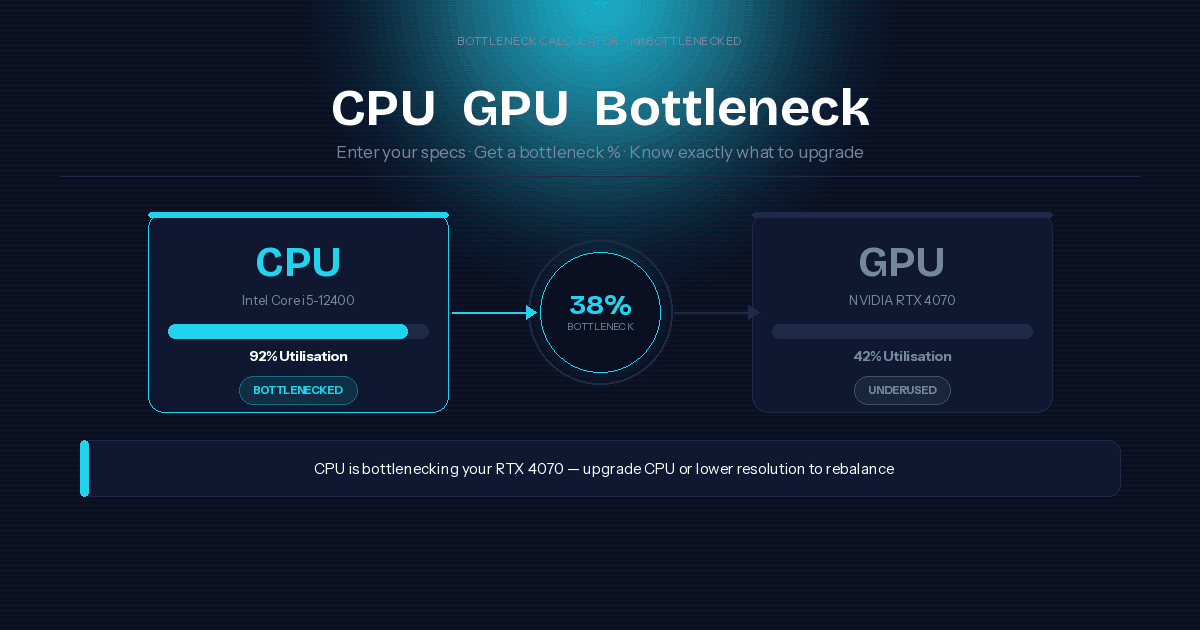
Not sure if you have a bottleneck? Here's how to do a bottleneck check in under 60 seconds. Our free PC bottleneck checker and bottleneck detector analyzes your exact CPU and GPU combo — no downloads, no sign-up required.
Whether you want to test for a CPU bottleneck, check for a GPU bottleneck, or just find out "am I bottlenecked?" — this tool gives you a clear, honest answer. It's the fastest way to check GPU-CPU compatibility and know exactly where your system stands.
Still asking "what's my bottleneck?" or "will it bottleneck my build?" — scroll back up, enter your specs, and hit Calculate. Your result will show exactly which component is the weak link and what to do about it.
isitBOTTLENECKED vs Other Bottleneck Calculators, Checkers & Testers
There are many bottleneck calculators. Many give a simple percentage that omits important details. We created our tool, isitBOTTLENECKED, to provide a clearer, more useful analysis that helps users make well-informed decisions.
The BIG WHY behind why we build this tool, if there are 10s of them already available!
When I started research on bottleneck calculators, two things came to me again and again: Facebook and Reddit users who openly say that these calculators are GARBAGE.
What? If there is a thing that's real too, and people are searching for it, how the hell are these tools described as garbage!
But from that time (3 August 2025) till NOW, I used every single bottleneck calculator. I personally checked how users discuss them in forums to understand why they can't make their users happy.
So after my months of researching, I came up with 5 things:
- 1: They make the bottleneck a big problem.
- 2: They just give a percentage, not a deep analysis.
- 3: They force users to buy components for better performance.
- 4: They don't give the point solution if the user's PC has a bottleneck.
- 5: They don't give honest recommendations to users if they want to build a pc for gaming, editing, etc.
Then I know why those guys are talking negatively about bottleneck checkers.
And as an entrepreneur, I have to stand out from the crowd by solving every issue they encounter in building a new pc or improving the older one, removing the bottleneck, and clearing the myths about pc bottlenecks in ONE PAGE.
So what this one page does for YOU:
This debunks the myth that a computer bottleneck is a major issue. In reality, having a bottleneck doesn't mean your PC is incapable of performing well or accomplishing great tasks.
Instead of just giving you a number, we explain what that number means to you. We provide clear explanations of whether you're facing a CPU bottleneck or a GPU bottleneck and what the practical implications are for your gaming or productivity workloads.
We know PC performance depends on many factors. While competitors only look at CPU vs. GPU scores, we include screen resolution, storage, and RAM in our main calculation. This gives results that match your real experience.
We don't push you to buy through our affiliate links just to make money. Instead, we offer honest recommendations backed by detailed analysis, pros, and cons—because better products deliver superior results, while poor ones lead to disappointing outcomes.
If our tool detects a bottleneck in your PC, we've got you covered 19 methods that minimize or eliminate bottlenecks in your computer.
And LAST thing we want to be very clear with all of you that the bottleneck service is just for general and inofrmation purpose, you can just begin your pc building journey with this bottleneck checker, but we highly recommend you don't fully depend on it.
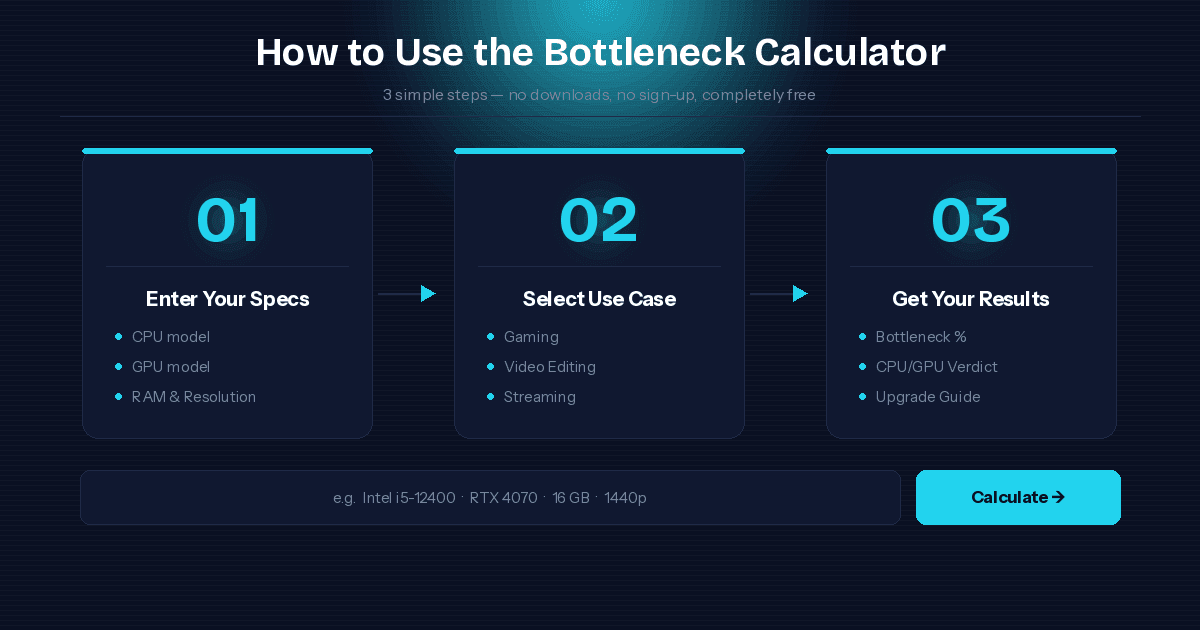
How to Use Our CPU GPU Bottleneck Calculator & Compatibility Checker
3 Simple Steps to Analyze Your Hardware Match
No downloads. No fees. Open the tool in your browser and do this:
- Enter your CPU model — Intel Core i5, i7, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 9, whatever you have.
- Enter your GPU — RTX 4070, RX 7800 XT, Arc, or any card in your system.
- Select your RAM size, resolution (1080p / 1440p / 4K), and primary use case — gaming, streaming, video editing, or everyday tasks.
Hit calculate. Done.
This free bottleneck testing tool works as a complete PC bottleneck tester and CPU GPU compatibility checker — giving you a verdict in seconds with zero technical knowledge required.
Decoding Your Results: What the Bottleneck Percentage Means
The bottleneck percentage tells you how mismatched your CPU-GPU combo is:
- 0–10% — Perfectly balanced. No changes needed.
- 10–20% — Minimal bottleneck. Barely noticeable in real-world gaming.
- 20–40% — Moderate imbalance. You're leaving performance on the table.
- 40%+ — Significant bottleneck. One component is dragging the whole system.
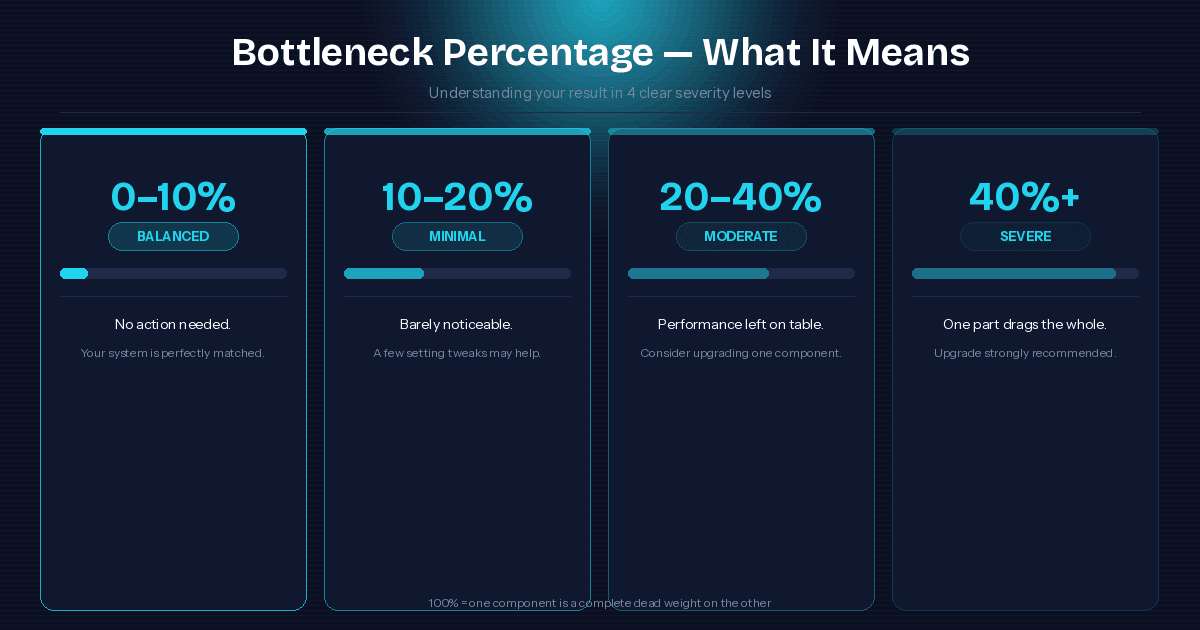
A 100% score means one component is a complete dead weight. The calculator also flags whether you're CPU-bound or GPU-bound — that distinction changes everything about what you should upgrade next.
Under the Hood: Our Calculation Methodology & Accuracy Features
The calculator cross-references a live database of real-world benchmark data from PassMark, UserBenchmark, and 3DMark stress tests. It uses an algorithm that weighs CPU core count, clock speeds, GPU VRAM, and architecture tier against your selected resolution and workload type. Want to know how accurate bottleneck calculators really are? The short answer: ours is built for precision, not guesswork — but no calculator replaces live monitoring with tools like MSI Afterburner or HWiNFO.

The Science of System Performance: What is a PC Bottleneck?
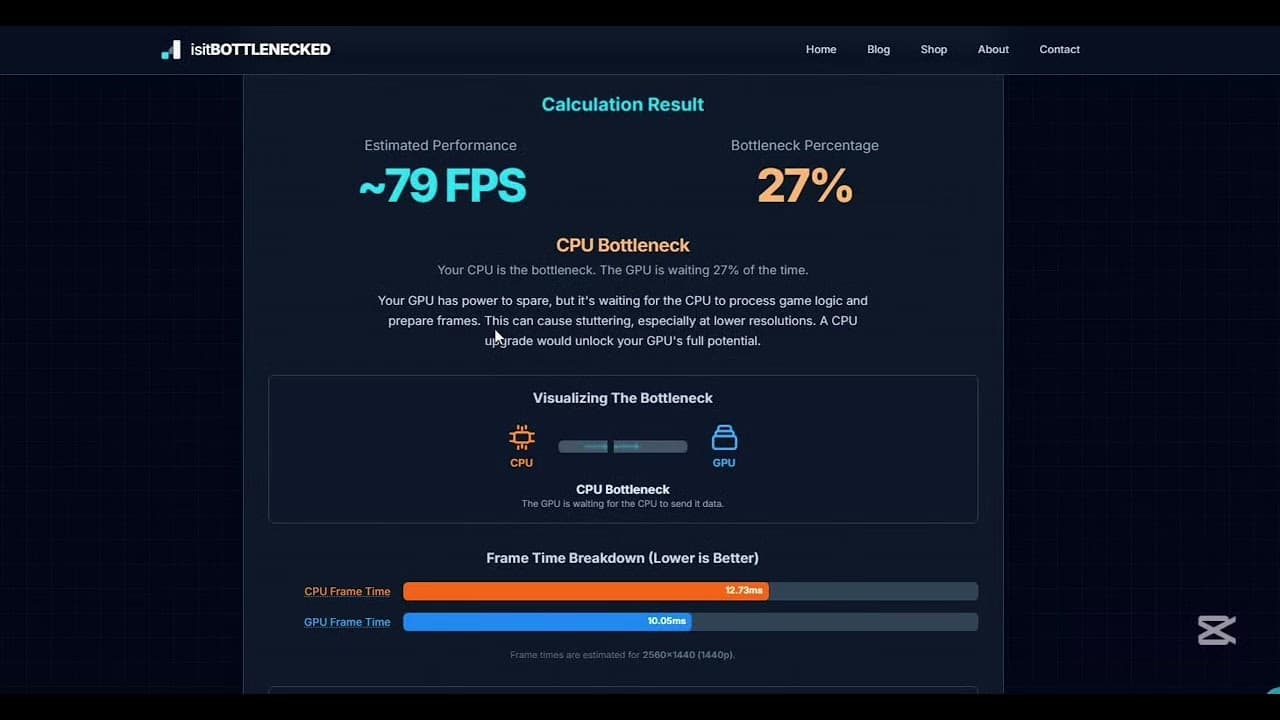
A visual explanation of what a PC bottleneck is and how it affects performance.
Think of your PC like a relay race. Your CPU passes the baton to your GPU. If one runner is slower than the other, the whole team suffers — no matter how fast the faster runner is. That's a bottleneck. The weakest link sets the ceiling for everything else.
A bottleneck happens when one component maxes out while another sits idle. You get frame drops, stuttering, choppy visuals, and micro-stutter even at "good" FPS numbers. It's the most frustrating kind of performance problem because your hardware isn't broken — it's just mismatched.
Why Hardware Balancing Matters for Gaming & Productivity
In gaming, balance determines whether you get smooth 144 FPS or laggy 60 FPS with stutters. In video editing — Adobe Premiere, Blender, DaVinci Resolve — it determines whether your exports take 3 minutes or 30. For streamers using OBS, a CPU bottleneck means dropped frames during encoding. For 3D creators, GPU bottlenecks mean slow renders. Getting the right CPU-GPU combo isn't just about raw specs — it's about matching components to your actual workload.
Deep Dive into Component Limitations (Causes & Fixes)
Processor Constraints (CPU Bottlenecking)
Your CPU handles game logic, physics, AI calculations, and draw calls. When it's overwhelmed — usually by CPU-intensive titles, simulation games, or heavy multitasking — you get high CPU usage with your GPU sitting below 80%. Common causes: outdated architecture, too few cores, low clock speeds, or background programs eating up threads. Understanding CPU core count vs. clock speed helps you pick the right processor for your workload.
Graphics Processing Limitations (GPU Bottlenecking)
GPU bottlenecks happen when your graphics card can't keep up with the resolution and texture demands you're throwing at it. You'll see your GPU pinned at 99% while your CPU chills at 40–60%. This is actually the ideal state for gamers — it means your CPU isn't the limiting factor. But if your GPU is old, low on VRAM, or underpowered, frame rates crater in demanding titles at 1440p or 4K.
System Memory Shortages (RAM Bottlenecks)
8GB RAM in 2026 is a liability. Modern AAA games routinely need 12–16GB. When your RAM fills up, your system starts using virtual memory on your drive — and that kills performance. Slow RAM speeds also hurt, especially in Ryzen builds where memory bandwidth directly affects performance. Running DDR5 vs. DDR4 matters more than most people realize. Always run dual-channel, and enable XMP/DOCP in BIOS.
Drive Speed Restrictions (Storage/SSD Bottlenecks)
A slow HDD doesn't cap your FPS directly, but it wrecks load times, causes stutters when streaming open-world assets, and slows your entire system's responsiveness. NVMe SSDs (Gen 4 M.2) are the standard for gaming PCs in 2026. If you're still on a SATA SSD or worse, an old hard disk, your storage is a silent bottleneck dragging down your experience.
Real-Time Diagnostic Guide: CPU vs. GPU Utilization Scenarios
Use Task Manager, MSI Afterburner, or HWiNFO to monitor live utilization while gaming.
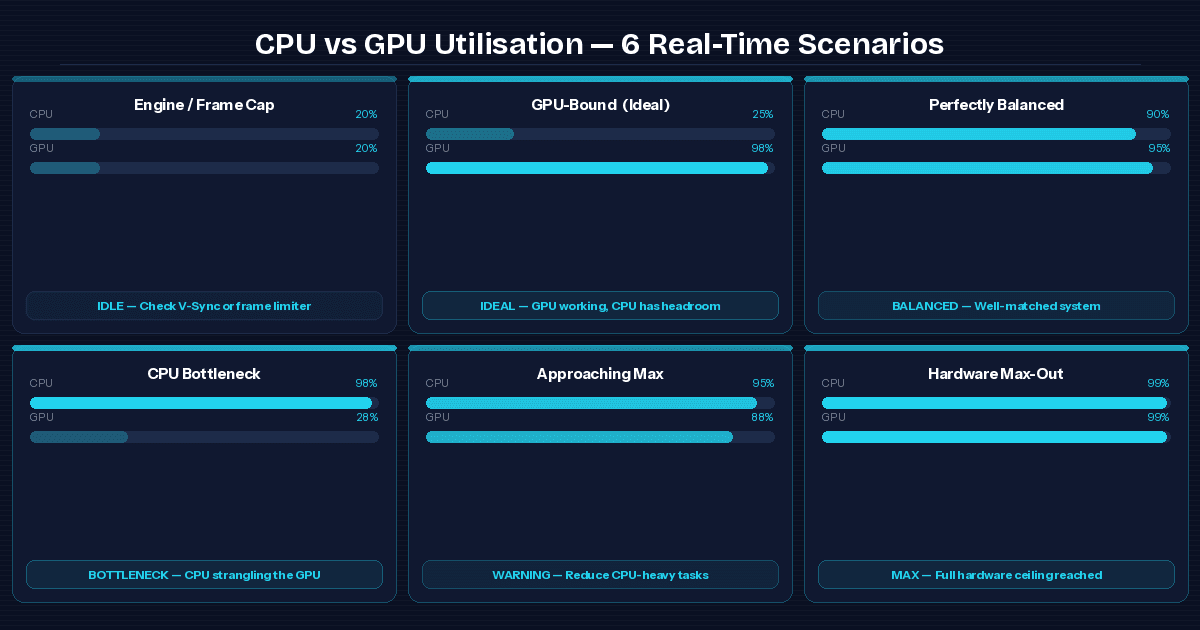
Low CPU & Low GPU Usage (Engine Constraints or Frame Limiters)
Both components are idle. Check for in-game frame caps, V-Sync being enabled, or a background program throttling resources. Sometimes the game engine itself is the culprit.
Low CPU & Maximum GPU Usage (The Ideal GPU-Bound State)
Your GPU is the limiting factor — this is exactly where you want to be. Your CPU has headroom, your GPU is working. Upgrade your GPU when you want more performance.
High CPU & Maximum GPU Usage (Perfectly Balanced System)
Both components are working near their limits. This is a well-matched system. You're getting close to the hardware ceiling — time to plan your next full upgrade.
Maximum CPU & Low GPU Usage (Severe CPU Bottleneck)
Your processor is strangling your graphics card. Common in CPU-intensive games like city builders and open-world RPGs. Your GPU is wasted. Fix the CPU first.
Maximum CPU & High GPU Usage (Approaching System Limits)
You're at the edge. Both components are near max. Reduce CPU-heavy background tasks, close OBS or Discord if streaming, and tweak in-game settings to shift load toward the GPU.
Maximum CPU & Maximum GPU Usage (Absolute Hardware Max-Out)
Full send. Both components are at 100%. Your system is delivering everything it has. If performance still isn't where you want it, it's time for a hardware overhaul. No software tweak will save you here.
Proven Strategies to Resolve System Bottlenecks
Software Tweaks: Resolution, DLSS, and In-Game Settings
Before you spend a dollar, try this: raise your resolution. Higher resolution shifts load to the GPU, relieving a CPU bottleneck. Enable DLSS (NVIDIA) or FSR (AMD) — upscaling at 1440p or 4K can recover 20–40% performance with minimal visual loss. Reduce CPU-heavy settings like draw distance, NPC density, and physics quality. Update your GPU drivers, BIOS, and firmware — outdated software causes phantom bottlenecks. For a full guide, check PC gaming performance optimization.
Hardware Upgrades: Overclocking vs. Component Replacement
Overclocking your CPU or GPU can squeeze 5–15% more performance with zero cost. But it comes with thermal risk — monitor your temperatures, clean your fans, replace thermal paste, and make sure your airflow and cooling (liquid AIO or quality heatsinks) can handle the extra heat. Learn how to safely overclock your CPU and GPU before pushing clocks. If overclocking isn't enough, then upgrade — but always fix the bottleneck side first. Dropping a new GPU into a CPU-bottlenecked system is wasted money.
Expert-Curated, Bottleneck-Free PC Build Templates
Here are three balanced build tiers for 2026:
- Lite ($500–$800): Intel Core i5 / Ryzen 5 + RTX 4060 / RX 7600 + 16GB DDR4 — solid 1080p gaming, zero bottleneck.
- Mid ($1,000–$1,500): Core i7 13600K / Ryzen 7 7700X + RTX 4070 Super + 32GB DDR5 — smooth 1440p, great for streaming.
- Advanced ($2,000–$3,000): Ryzen 9 7800X3D + RTX 4080 / RTX 5070 + 32GB DDR5 — 4K gaming and content creation with room to breathe.
Each combo is matched for balanced performance. No weakest link. No wasted hardware.
FAQs
What is a bottleneck in a computer system?
A bottleneck is when one component maxes out and limits the performance of every other component. The slowest part sets the ceiling.
Will it bottleneck my system?
That depends on your specific CPU and GPU combination, your target resolution, and your workload. Use our free bottleneck checker above to get an instant answer. As a general rule: pairing a high-end GPU with an older, low-core-count CPU almost always creates a CPU bottleneck in modern games — especially at 1080p where CPU demands are highest.
Am I bottlenecked right now?
The fastest way to find out is to run our free PC bottleneck test above, then cross-check with a live monitoring tool like MSI Afterburner. If your CPU is above 90% while your GPU sits below 70%, you have a CPU bottleneck. If your GPU is maxed and your CPU is relaxed — that's actually the ideal GPU-bound state for gaming.
Can my graphics card be a bottleneck?
Yes. If your GPU can't handle your resolution or graphics settings, it limits your FPS — even if your CPU is powerful.
Can the CPU be a bottleneck?
Absolutely. A slow or outdated processor caps how fast your GPU can receive and process data, causing wasted GPU potential and stuttering.
How can I tell if my PC has a bottleneck?
Monitor CPU and GPU usage while gaming using MSI Afterburner or HWiNFO. If one is at 99% while the other is below 70%, you have a bottleneck. Our how-to guide walks you through it step by step.
What is a CPU bottleneck? And what causes it?
A CPU bottleneck happens when your processor can't feed data fast enough to your GPU. Causes: too few cores, low clock speed, outdated architecture, or too many background tasks.
What is a GPU bottleneck? And what causes it?
A GPU bottleneck occurs when your graphics card can't render frames fast enough for your display. Causes: insufficient VRAM, outdated card, or running too high a resolution for your GPU tier.
CPU vs GPU bottleneck: What's the difference?
A CPU bottleneck means your processor is the limiting factor. A GPU bottleneck means your graphics card is. Here's the full breakdown with real-world examples.
Why is it important to identify bottlenecks in my PC?
Because upgrading the wrong part wastes money. Knowing your bottleneck tells you exactly what to fix — no guessing, no random disappointment.
How does the Bottleneck Calculator work?
It compares your CPU and GPU benchmark scores against a real-world database, factoring in your resolution and workload, then outputs a bottleneck percentage and upgrade recommendation.
Are bottleneck calculators completely accurate?
They're estimates — not perfect. They're based on theoretical benchmarks and component scoring algorithms. Real-world factors like thermal throttling, driver issues, and background software affect actual performance. Use live monitoring alongside any calculator result.
Does the Bottleneck Calculator consider the latest games?
Yes. The database is updated regularly to reflect modern GPU and CPU performance in current-gen titles and resolutions.
Can RAM or storage cause a bottleneck?
Yes. Insufficient or slow RAM forces your system to use disk swap, killing responsiveness. A slow HDD causes stuttering in open-world games that stream assets in real time.
How do I know if my system has a bottleneck?
Use the calculator for a quick estimate, then verify with live monitoring tools like HWiNFO, GPU-Z, or Task Manager.
What is an acceptable bottleneck percentage?
0–10% is ideal. Up to 20% is fine for most gaming scenarios. Over 40% means you need to act.
How to fix a CPU bottleneck?
Overclock your CPU, reduce CPU-heavy in-game settings, close background programs, or upgrade to a processor with more cores and higher clock speeds. Full guide: how to fix CPU/GPU bottlenecks.
How to fix a GPU bottleneck?
Lower your resolution or graphical settings to reduce GPU load. Long-term: upgrade to a more powerful card with more VRAM for your target resolution.
Can upgrading one component resolve a PC bottleneck?
Usually yes — if you upgrade the right one. Upgrading the bottlenecked component fixes the imbalance. Upgrading the already-fast component changes nothing.
Should I upgrade my CPU or GPU first?
Upgrade whichever is bottlenecking your system. If you're CPU-bound, fix the CPU. If you're GPU-bound, upgrade the GPU. The calculator tells you exactly which.
Does overclocking help with bottlenecks?
It can reduce them, especially on the CPU side. But it's a tweak, not a cure. If your bottleneck is severe (40%+), overclocking alone won't close the gap.
Can SSDs or HDDs cause performance bottlenecks?
Yes — primarily in load times, game stuttering, and system responsiveness. NVMe SSDs dramatically reduce these issues compared to HDDs or older SATA drives.
Stop guessing. Stop spending money on parts that don't fix your actual problem. Use our CPU GPU Bottleneck Calculator right now to get a real bottleneck percentage, a clear compatibility verdict, and smart upgrade guidance — so every dollar you spend actually improves your system.
Whether you searched for a bottleneck calculator, a bottleneck checker, a bottleneck tester, a PC bottleneck detector, or just typed "is it bottlenecked?" — you've found the right tool. isitBOTTLENECKED covers every use case: CPU bottleneck test, GPU bottleneck check, CPU GPU compatibility checker, PC bottleneck test, and honest upgrade advice — all free, all in one place.